Thursday, October 16, 2014
Motorcycle Alarm With Transistor Circuit Diagram
Veroboard Layout
Wiring diagram 1965 Ford Mustang
Simple 150W Amplifier Circuit Diagram
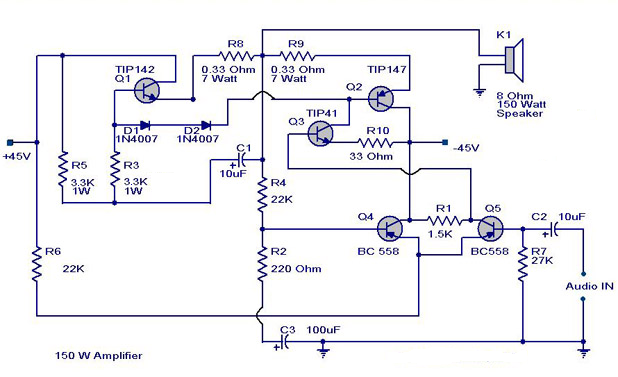
Notes.
- Remember TIP 142 and 147 are Darlington pairs .They are shown as conventional transistors in figure for ease.So don’t get confused.Even though each of them have 2 transistors ,2 resistors and 1 diode inside ,only three pins ,base emitter and collector are coming out.Rest are connected internally.So its quite OK to assume each of them as transistor for ease.
- Use a well regulated and filtered power supply.
- Connect a 10K POT in series with the input as volume control if you need.Not shown in circuit diagram.
- All electrolytic capacitors must be rated at least 50volts.
Power supply for this circuit.
A +40/-40 unregulated dual supply for powering this amplifier project is shown below. This power supply is only enough for powering one channel and for stereo applications double the current ratings of the transformer, diodes and fuses.
Wednesday, October 15, 2014
Burglar Alarm With Timed Shutoff Circuit Diagram
Simple DPA 220 schematic
The T7 and T8 are fast, switching application types.
T9 and T10 have to be fast and must hold a high voltage, thus the best are the "video" types - BF469/470. T15 and T16 are the same types.
The C9, C10 and C15 should stand voltages higher than usual 50 V - I dont know why.
D3 to D6 can be any silicon type, not Scottky, the ones listed below are just all-purpose low-current ones for 150 V. These diodes should be rather fast - "switching types".
The T11 and T12 stabilize the BIAS current for the power stage. T11 also serves as a temperature sensor, and is mounted to the cooler of power transistors.
T13 and T14 secure the output current - in cooperation with R38 and R39.
The output transistors used here are Tesla types - Tesla is a former local devices manufacturer - the pair in each branch can be replaced with a single power darlington, like BD649/BD650. They should have Pc > 150W, Ic > 15A, Uceo > 100V.
In this case obviously the R38+R40 / R39+R41 must be connected parallel. These resistors should be able to absorb high power - at least 2 W, but Id use 5W ones.
The output filter improves stability of the amp when working with complex impedance of speakers - it is quite important. The resistors are high-power ones again, the coil is 13 turns of a 1.2 mm wire on a 8 mm thorn (diameter). R43 is placed coaxially in the coil.
The schematic also includes power supply capacitors and rectifier - the capacitors size is not crucial, generally the bigger the better. The rectifier originally consists of four silicon 10A diodes, but you can use whatever you have - rectifier bridge etc. The trafo should be a 2 * 30 V / 7 A type so that you have +/- 40 V on the power supply capacitors.
In the scheme theres also a thermistor that is supposed to be connected to some additional circuits that secure temperature and other things. The complementary input stage of DPA amps is an unmistakable heir of earlier designs published by Mr. Borbely in several issues of Volume 1984 of the Audio Amateur.
Monday, October 13, 2014
Volvo 700 B230K Engine Ignition System Wiring Diagram
During the production between 1982–1990, the Volvo 700 series (760, 740, 780) were available in many different engine types and capacities, among others are 2.3 L B23ET 173 hp (129 kW) turbo I4; 2.3 L B230FT 156/165 hp turbo I4; 2.8 L B280F 147 hp V6 and 2.4 L D24TIC 115 hp (86 kW) turbo diesel I6. Below schematic depicts the 1982 Volvo Volvo 700 B230K Engine Ignition System Wiring Diagram.
| 1. Battery 2. Ignition Switch 4. Ignition Coil 5. Distributor 6. Spark Plugs 11. Fuse box 29. Positive Terminal Board 81. AC Pressure Switch 86. Rev Counter 156. Radiator Fan Motor 200. AC Compressor Solenoid 202. Climate Control 218. Knock Sensor | 224. Radiator Fan Thermostat 260. Control Unit 267. Test Connector 271. Fuel Cut-off Solenoid 272. Micro switch 273. Temperature Sensor 293. Idling Compensation relay 419. Power Stage A. Connector, RH A-Post B. Connector, LH A-Post C. Connector, at LH Wheel Housing D. Ground Terminal on Intake Manifold E. Connector at LH Wheel Housing |
Latest new Oxygen Sensor Simulator Oxygen Simulator Sensor

The schematic diagram for the simulator. Closing the switch engages the simulator. Turning the knob clockwise simulates a lean condition, turns the LED off, and the car should start running rich to compensate. The big "V" is a digital voltmeter (not shown in the pictures). Using a smaller value for C1, perhaps 4.7 uF, will make the circuit oscillate faster and might be more like a real oxygen sensor (a new sensor switches more often than an old one).
The schematic diagram of the adapter cable and oxygen sensor. Note the heater is shown as a resistor, mine measured about 7 ohms.
Power Monitor Circuit Diagram
Sunday, October 12, 2014
Stereo FM Transmitter Based BH1417 Chips diagram
Stereo FM Transmitter Based BH1417 Chips
This electronic circuit is a latest BH1417 FM Transmitter design from RHOM that includes a lot of features in one small package. It comes with pre-emphasis, limiter so that the music can be transmitted at the same audio level, stereo encoder for stereo transmission, low pass filter that blocks any audio signals above 15KHz to prevent any RF interference, PLL circuit that provides rock solid frequency transmission (no more frequency drift), FM oscillator and RF output buffer.
There are 14 possible transmission frequencies with 200KHz increments that users can select with a 4-DIP switch. Lower band frequencies start from 88.7 up to 89.9 MHz, and upper band frequencies start from 107.7 up to 108.9 MHz.

BH1417 can be supplied with 4 - 6 voltage and consumes only around 30mA, providing 20mW output RF power. BH1417 provides 40dB channel separation which is pretty good, although older BA1404 FM Transmitter chip provides slightly better 45dB channel separation.

BH1417 is only available in SOP22 IC case so this may be an inconvenience for some folks. On the other hand, because the chip is smaller than regular DIP-based ICs it is possible to fit the entire transmitter on a small PCB.
The bad news is that BH1417 requires 7.6MHz crystal oscillator, which is very hard to find. The good news is that you can use 7.68 MHz crystal instead, which is easier to find. In fact our BH1417 transmitter prototype (schematic shown above) uses 7.68 MHz crystal. This has absolutely no effect on stereo encoding process, we have tested it and stereo sound is crystal clear. The transmitted frequency on the other hand will be shifted up by exactly 1MHz (example: 88.1 MHz to 89.1 MHz) which is perfectly fine. The frequencies that are used in this project have been adjusted by 1MHz already so no additional conversion is necessary.
BH1417 chip may also be used a stand alone stereo encoder. The advantage of that is that you have full freedom of using a transmitter & amplifier of your choice. You will still have a pre-emphasis, limiter, stereo encoder and low pass filter in one small package because very few external components are required for these blocks. PIN 5 is MPX output that can be directly connected to an external FM transmitter through a 10uF cap.
Parts List:
1x BH1417 - Stereo PLL Transmitter IC (Case SOP22) (datasheet)
1x 7.68 MHz Crystal
1x MPSA13 - NPN Darlington Transistor
1x 2.5 Turns Variable Coil
1x MV2109 - Varicap Diode
1x 4-DIP Switch
ANT - 30 cm of copper wire
1x 22K Resistor
7x 10K Resistor
1x 5.1K Resistor
2x 3.3K Resistor
1x 100 Ohm Resistor 1x 100uF Capacitor
3x 10uF Capacitor
2x 1uF Capacitor
1x 47nF Capacitor
3x 2.2nF Capacitor
1x 1nF Capacitor
1x 330pF Capacitor
2x 150pF Capacitor
1x 33pF Capacitor
2x 27pF Capacitor
1x 22pF Capacitor
2x 10pF Capacitor
Specifications:
Supply Voltage: 4 - 6V
Transmission Frequency: 87.7 - 88.9MHz, 106.7 - 107.9MHz (200kHz steps)
Output RF Power: 20mW
Audio Frequency: 20 - 15KHz
Separation: 40dB
Power Consumption: 30mA
Frequency Selection / Calibration
Frequency selection is very straight forward. Simply select transmission frequency at which you would like to transmit, set the combination for 4-DIP switch and BH1417 will immediately tune to that frequency. If you cant hear the transmitted audio signal on your FM receiver then re-adjust 2.5 turn variable coil until you can hear the signal. If you have a laboratory power supply you may try to vary the voltage supply from 4 to 6V. While doing that BH1417 will automatically vary the voltage for MV2109 varicap diode making sure that theres no frequency drift.

Power Supply 5V 1 3 3A by LM2575
Read More Source:
http://www.mct.net/product/power1.html
Friday, October 10, 2014
FAN302HL bassed 5 volt switching power supply circuit project
A very simple 5 volt switching power supply electronic circuit project can be designed using FAN302HL highly integrated PWM controller integrated circuit, that provides several features to enhance the performance of general flyback converters.
The constant-current control, of the FAN302HL proprietary topology enables simplified circuit designs without secondary feedback circuitry for battery charger applications.
This 5 volt switching power supply electronic circuit project accepts a wide range input voltage from 90 to 265 VAC and will provide a 5 volt regulated output at a maximum output current of 1.2 ampere .
A proprietary Burst-Mode function with low operation current minimizes standby power consumption.
The FAN302HL controller also provides several like protections : VDD Over-Voltage Protection (Auto-Restart) ,VS Over-Voltage Protection (Latch Mode) , Fixed Over-Temperature Protection .
The most difficult part that is require in this project is the transformer.
W1 is four winds; for each wind of turns, refer to table bellow. Add one insulating tape between the first and second layers.
W2 is wound two layers and uses triple-insulated wire: end of positive fly line is 3.5cm, layer end of negative fly line is 2.5cm.
W3 is spares winding in one layer.
W4 is wound in the core of the outermost layer and sparse winding.
Thursday, October 9, 2014
Circuit measurements temperature by diode 1N4148
measurements temperature by diode 1N4148
temperature by diode 1N4148 and ic 741.
easy to make and use.
Out to Voltmeter.
*** Low cost too !
When I wants the circuit takes the temperature to are simple. I uses Diode 1N4148 be formed check the temperature. By when feed voltage change it. It is have current flow be stable. When the temperature that Diode, change make Voltage. At it modifies with VR1 and VR2 fine decorate for show that is correct most fining decorates. The important I uses the temperature certainly compare with accurate temple. By compare with reserve 0 the degree Celsius per 0 Volt. For the certainty advises that, should use Digital Voltage Meter. Show well almost forget the important point should. Give power supply Regulator high-quality , such as IC 7815 and IC 7915 etc. Try usable this circuit sees, regard good base of the circuit takes the temperature sir.
latest circuit and explanation of Basic UPS Power Supply
Email: anc@mitedu.freeserve.co.uk
Description
This circuit is a simple form of the commercial UPS, the circuit provides a constant regulated 5 Volt output and an unregulated 12 Volt supply. In the event of electrical supply line failure the battery takes over, with no spikes on the regulated supply.
Notes:
This circuit can be adapted for other regulated and unregulated voltages by using different regulators and batteries. For a 15 Volt regulated supply use two 12 Volt batteries in series and a 7815 regulator. There is a lot of flexibility in this circuit.
TR1 has a primary matched to the local electrical supply which is 240 Volts in the UK. The secondary winding should be rated at least 12 Volts at 2 amp, but can be higher, for example 15 Volts. FS1 is a slow blow type and protects against short circuits on the output, or indeed a faulty cell in a rechargeable battery. LED 1 will light ONLY when the electricity supply is present, with a power failure the LED will go out and output voltage is maintained by the battery. The circuit below simulates a working circuit with mains power applied:
Between terminals VP1 and VP3 the nominal unregulated supply is available and a 5 Volt regulated supply between VP1 and VP2. Resistor R1 and D1 are the charging path for battery B1. D1 and D3 prevent LED1 being illuminated under power fail conditions. The battery is designed to be trickle charged, charging current defined as :-
where VP5 is the unregulated DC power supply voltage.
D2 must be included in the circuit, without D2 the battery would charge from the full supply voltage without current limit, which would cause damage and overheating of some rechargeable batteries. An electrical power outage is simulated below:
Note that in all cases the 5 Volt regulated supply is maintained constantly, whilst the unregulated supply will vary a few volts.
Standby Capacity
The ability to maintain the regulated supply with no electrical supply depends on the load taken from the UPS and also the Ampere hour capacity of the battery. If you were using a 7A/h 12 Volt battery and load from the 5 Volt regulator was 0.5 Amp (and no load from the unregulated supply) then the regulated supply would be maintained for around 14 hours. Greater A/h capacity batteries would provide a longer standby time, and vice versa.
Circuit Switching Regulators Using LM2575 and LM2577
Switching regulators are available is different circuit configurations including the flyback, feed-forward, push-pull, and non-isolated single-ended or single-polarity types. Also, the switching regulators can operate in any of three modes – step-down, step-up, or polarity inverting.
rovide the active functions for step-down (back) switching regulator, capable of driving a1A load with excellent line and load regulation. These devices are available in fixed output voltages of 3.3V, 5V, 12V, 15V and an adjustable output version.
Requiring a minimum number of external components, these regulators are simple to use and include internal frequency compensation and a fixed-frequency oscillator. LM 2575 series offers a high-efficiency replacement for popular 3-terminal linear regulators. It substantially reduces the size of the heat sink, and in many cases no heat sink is required. Fixed output voltage version is illustrated in figure.
The National Semiconductor LM 1577/LM 2577 are monolithic ICs that provide all of the power and control functions for step-up (boost), fly back, and forward converter switching regulators. The device is available in three different output voltage versions: 12 V, 15 V and adjustable.
Simple Toy Organ Circuit based Timer IC 555
This is a very simple toy organ circuit which built based timer IC 555. It only contains of several components, even a newbie can build this circuit easily. This circuit generates a tone according to the button being pressed.
This easy build toy organ can be powered with 6V battery supply or commonly general purpose power supply. Only 1 button can be pressed at a time, that’s why it is called a monophonic organ. You can change the 1k resistors to produce a more-accurate scale. You also can add new tones by add some switchs and 1k resistors. If you need a louder sound, you can add an amplifier on the output.
Wednesday, October 8, 2014
Low Cost Fire Alarm Circuit and explanation Using Transistor

Notes:
- The Preset R1 can be used to desired temperature level for setting the alarm ON.
- This is not a latching alarm,ie; when the temperature in the vicinity of the sensor decreases below the set point the alarm stops.
- The circuit can be powered using a 9V battery or a 9V battery eliminator.
- All capacitors are electrolytic and must be rated at least 10V.
- The load can be connected through the C,NC,NC points of the relay according to your need.
- The calibration can be done using a soldering iron,and a thermo meter. Switch ON the power supply.Keep the tip of soldering iron near to the Q1.Same time also keep the thermometer close to it.When the temperature reaches your desired value adjust R1 so that relay gets ON.
LM1877 bassed Audio power amplifier circuit and explanation
This audio amplifier circuit is designed to deliver 2W per channel continuous into 8Ω loads. The LM1877 is designed to operate with a low number of external components, and still provide flexibility for use in stereo phonographs, tape recorders and AM-FM stereo receivers, etc.
Each power amplifier is biased from a common internal regulator to provide high power supply rejection, and output Q point centering. The LM1877 is internally compensated for all gains greater than 10.
This audio amplifier circuit can be powered from a wide input voltage range from 6 volt up to 24 volts .
For this audio power amplifier circuit diagram you must use a 8 ohms speaker .
Sunday, October 5, 2014
Circuit digital clock circuit,
This signal is decoded in CPLD and eight kinds of signals are made. This time, six kinds are used. Only the transistor which corresponds to the L level decoder output becomes ON condition. The LED which is connected with the transistor becomes a lighting-up possible condition. In the tens-hour display, only “1″ is displayed. So, I put the display of AM/PM. 74HC138 can be used for the 3-8 decoder, too. Segments of the lighting-up of each digit are controlled using 7 ports of RC6 from RC0 of PIC. The output of these ports is common to all the LEDs.
However, only the LED of the digit which was specified by RA0-2 is controlled in the lighting-up. The LED lights up when the RC port is an L level. The brightness of the LED depends on the kind of the LED. When the brightness is different extremely, the resistors which are connected with the RC ports should be separated. This time, because it is approximately the same brightness, resistors are made common. Because the maximum voltage which is applied to the pin of PIC is 5V, I make the power of the LED 5V.
2N3055 TIP41 CA3140 Lab Power Supply 0 30V 2A
This is the schematic of the 30V/2A power supply I use in my own lab.It may look very complex, but it really isn’t very difficult to understand: it uses only the knowledge we’ve learned in the previous lessons.
The top part looks like the power supply we built in Lesson 7: the transformer L1 transforms the outlet voltage to a safe 30V, which is rectified by bridge rectifier G2 and smoothed by capacitor C5. Transistors T3 and T6 form a darlington transistor. This darlington replaces transistor T1 in Lesson 7. However, the base voltage is not controlled by a simple potmeter, but by an ‘electronic potmeter’ with voltage feedback. The advantage of this feedback is a load-independent output voltage.
LM317 Overvoltage Protection Circuit
Such a broadcast would be absolutely difficult to find, so I advised this, it is a simple two transistor ambit which will about-face off the achievement should the voltage accession aloft 6.2v (this can be afflicted by selecting a altered amount of zener diode ).
Components are as follows:
ZD1 =3D 6.2v Zener diode (you can change this to any value, the ambit will about-face off the achievement if the ascribe voltage raises aloft the amount of the zener diode)
R1 = 1K Resistor (this can be of any ability rating, it carries actual little power)
R2 = 1K Resistor (this can be of any ability rating, it carries actual little power)
T1 = Low ability NPN Transistor (BC108 or BC547 will do fine)
T2 = NPN transistor transistor able of switching the accessories you are active (BFY51 or BC140 can about-face 1 Amp, which is the best the voltage regulator ambit can handle)
It is appropriate to analysis this ambit with a voltmeter, boring accretion the voltage on the regulator ambit and accomplish abiding that this ambit switches off the achievement back the amount of the zener diode is reached, afore active in your big-ticket equipment. This ambit is advised to be acclimated with the voltage regulator acquaint by Matthew Hewson, my overvolatge add-on ambit is apparent with the aboriginal below:
Saturday, October 4, 2014
500W low cost 12V to 220V Inverter

Attention: This Circuit is using high voltage that is lethal. Please take appropriate precautions
How to calculate transformer rating
The basic formula is P=VI and between input output of the transformer we have Power input = Power output
For example if we want a 220W output at 220V then we need 1A at the output. Then at the input we must have at least 18.3V at 12V because: 12V*18.3 = 220v*1
So you have to wind the step up transformer 12v to 220v but input winding must be capable to bear 20A.
SG3524 PWM Inverter Circuit 250W

1 5 Volt Tracking Transmitter
If you like to have the tracker around the 88Mhz you can do that by spreading the windings from the home-made coil just a bit (1/2 a millimeter or so). Anyways, play with it and learn. It is a nice project. The 12-inch antenna can be anything, it is not really that critical. I used a piece of 22 gauge flexible wire. I havent checked the range but will do that shortly.
* For stability, use a NPO types for C2 & C4.
* Resistance tolerance for R1 should be 1 or 2%.
* Frequency range is the usual 87-109Mhz on the FM dial.
* The coil is made from 22 ga hookup wire, like the solid Bell phone wire. Leave the insulation on.
* The LED is the High Brightness type for maximum illumination.
Partlist
C1= 100uF electrolytic capacitor
C2= .01uF disc capacitor
C3= 4 to 40 pF trimmer capacitor
C4= 4.7 pF trimmer capacitor
L1= 0.1 uH, 6 to 8 turns of 22 gauge hookup wire close wound around a 1/4" diameter non-conductive core, such as pencil
IC1= LM3909 LED flasher
LED1= Red LED
Q1= 2N3904 NPN silicon transistor
R1= 10K
Antenna= 10 to 12 inches of hookup wire
Friday, October 3, 2014
Ramp Generator Circuit using NE555
Charging current produced by PNP constant current source is
iC = Vcc-VE / RE
where VE = R2 / (R1 + R2) * VCC + VBE
Thursday, October 2, 2014
Circuit Diagram FM Antenna Booster

This is a low cost fm antenna booster that can be used to listen to programmes from distant FM stations clearly. The antenna fm booster circuit comprises a common-emitter tuned RF preamplifier wired around VHF/UHF transistor 2SC2570 (C2570).
Assemble the circuit on a good-quality PCB (preferably, glass-epoxy). Adjust input/output trimmers (VC1/VC2) for maximum gain.
Input coil L1 consists of four turns of 20SWG enamelled copper wire (slightly space wound) over 5mm diameter former. It is tapped at the first turn from ground lead side. Coil L2 is similar to L1, but has only three turns. Pin configuration of transistor 2SC2570 is shown in the fm antenna booster schematic.
Dark Room Timer Circuit
but Let’s not go into that here. Suffice it to say that normal lights cannot be used in a darkroom when photographs are being developed not even if you drop your glasses! The circuit here is a simple, inexpensive design for a darkroom torch (or light) that can be mounted in a case small enough to fit into your pocket even with a 9 V battery included. It gives enough light for note-taking or finding this or that in a darkroom, but the light is emitted by three special yellow LEDs which can safely be used near black/white or colour paper. Red LEDs are used for orthochromatic material (we had to look it up too, it means giving correct relative intensity to colours in photography!). An energy saving circuit is included that automatically switches the lamp off when the ambient light is above a certain level. The diagram for the circuit makes it look like a mini power supply. When the circuit is switched on with S1 T2 conducts and provides, in turn, a base drive current to transistor T1. This transistor then supplies the base current for T2 via R5 and P1. i Switching S‘l off causes C1 to deliver a negative pulse to the base of T2 and this transistor then stops conducting.
Tl also stops conducting and the LEDs go out. The energy saving circuitry requires the addition of just one component, the LDR. When enough light falls on it the LDRs resistance causes T2 to switch off and extinguish the LEDs. The Iight level at which this happens is set by means of preset P1 Q LEDs D3 . . . D5 must be high efficiency types and are either red or yellow depending on what sort of photographic paper is used. There are various high intensity LEDs available, although the light intensity level can also be changed by varying the current flow through T1 (by substituting another value of resistor for R1 ). With the values stated about 20 mA flows through the LEDs and, seeing as the current consumption when the LEDs are off is only a few nA, the 9 V battery should last quite a while. Finally it is important to remember that some types of photographic paper are sensitive to all colours, including red and yellow, so check this before using the lamp.

Wednesday, October 1, 2014
True RMS Detector Circuit
Mathematically, the RMS value of a function is obtained by squaring the function, averaging it over a time period I` and then taking the square root:
Vrms = root of (1/T integrated from 0 to t * V^2dt)
ln a practical sense this same technique can also be used to find the RMS value of a waveform. Using two multipliers and a pair of op amps, an RMS detector can be constructed. The first multiplier is used to square ts. input waveform. Since the output of the multiplier is a current, an op amp is customarily used to convert this output to a voltage. The same op amp may also be used to perform the averaging function by placing a capacitor in the feedback path. The 1 second op amp is used with· a multiplier as the feedback element to produce the square root configuration. This method eliminates the thermal-response time that is prevalent in most RMS measuring circuits. The input voltage range for this circuit is from 2 to 10 Vpk. For other ranges, input scaling can be used. Since the input is dc coupled, the output voltage includes the dc components of the input waveform.



